COSLIC Application in Networking
In the Internet era, big data, IoT, cloud services, and more are driving ever-increasing demand for network traffic and bandwidth. As we enter the Web 3.0 era, residential fiber broadband is gradually replacing traditional ADSL networks. The network architecture primarily utilizes passive optical network (PON) technology. PON is a point-to-multipoint fiber optic access technology. For example, in a fiber home (FTTH) setup, a network service provider uses an optical signal splitter to split the signal into multiple paths and provide it to multiple optical network terminals (ONTs). Each ONT provides a variety of output ports, such as wired RJ45, wireless Wi-Fi, and even voice FXS/RJ11 interfaces, to connect different devices. ONTs are commonly referred to as optical modems.
Network Application Architecture Layer Diagram:
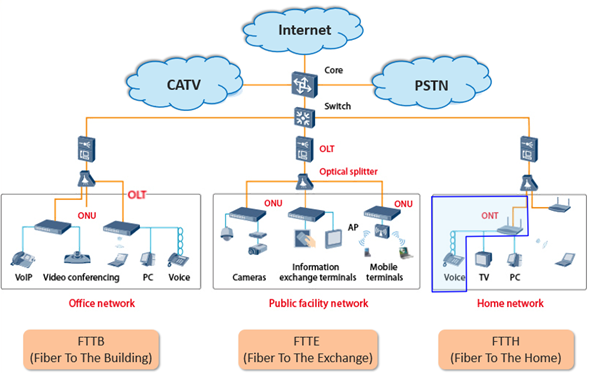
Optical technology plays a pivotal role in increasing network bandwidth, transitioning to fiber to the home (FTTx), and ultimately evolving to room-level deployments. In addition to enabling high-speed internet connectivity, it also supports voice communications. Essential to the architecture of these applications is the digital-to-analog conversion FXS chip known as Coslic. Coslic connects the main control chip to the phone, ensuring efficient communication and integration within the network infrastructure.
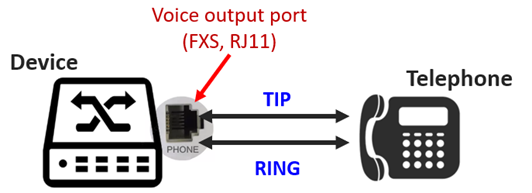
FXS (Foreign Exchange Station) Peripheral Equipment and User Phone Interface:
The FXS interface directly connects to standard telephones, fax machines, or similar devices, providing ring voltage, standby voltage, and dial tone to the phone. Common FXS interfaces use RJ-11 connectors, with outputs as two analog signals, TIP and RING.
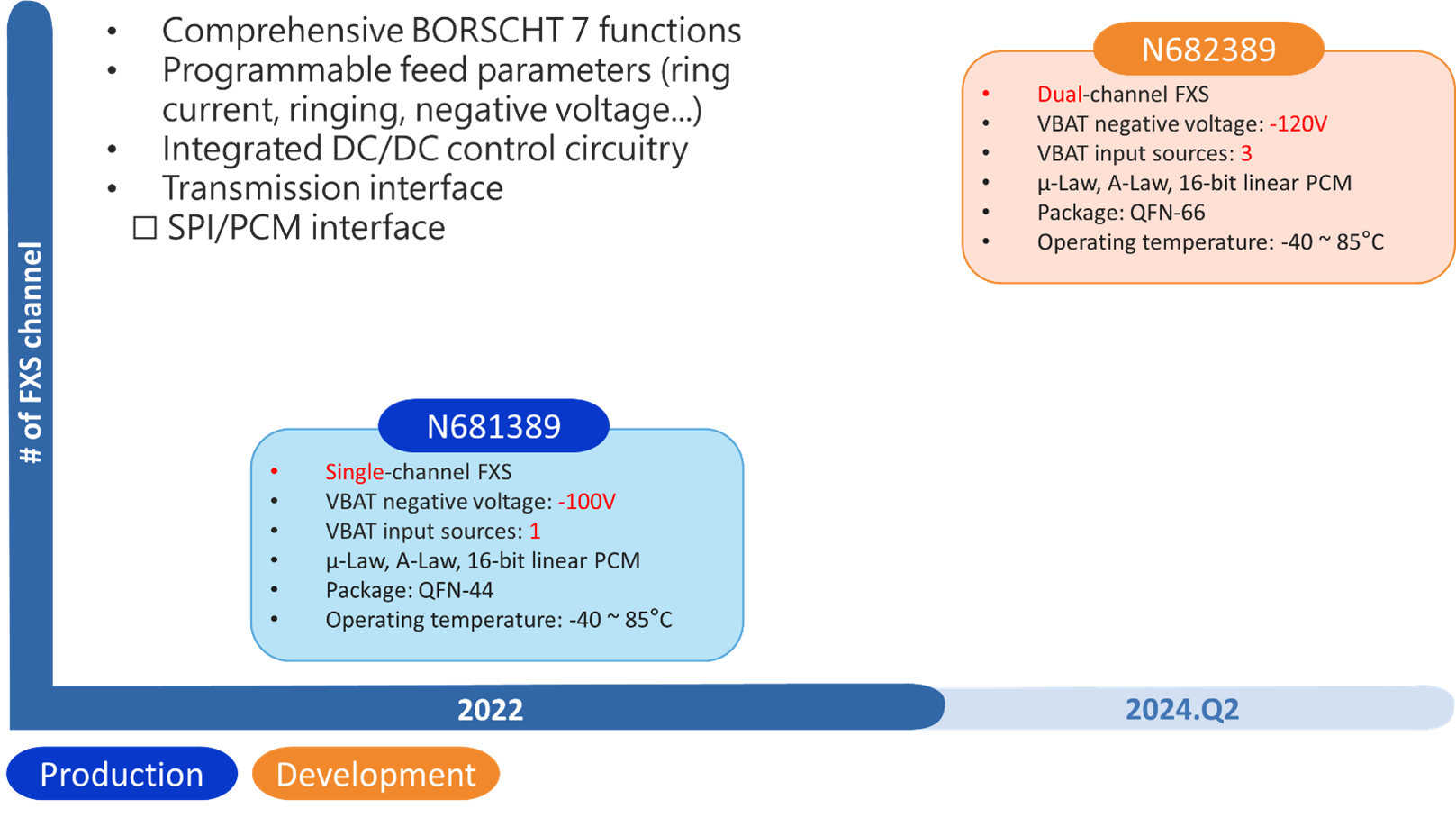
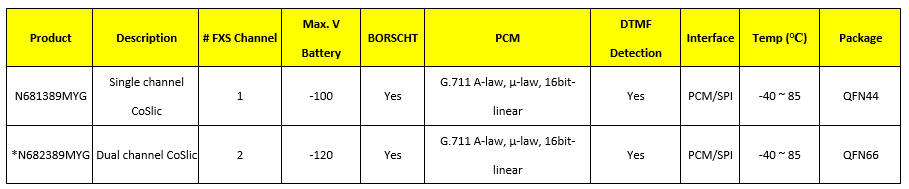
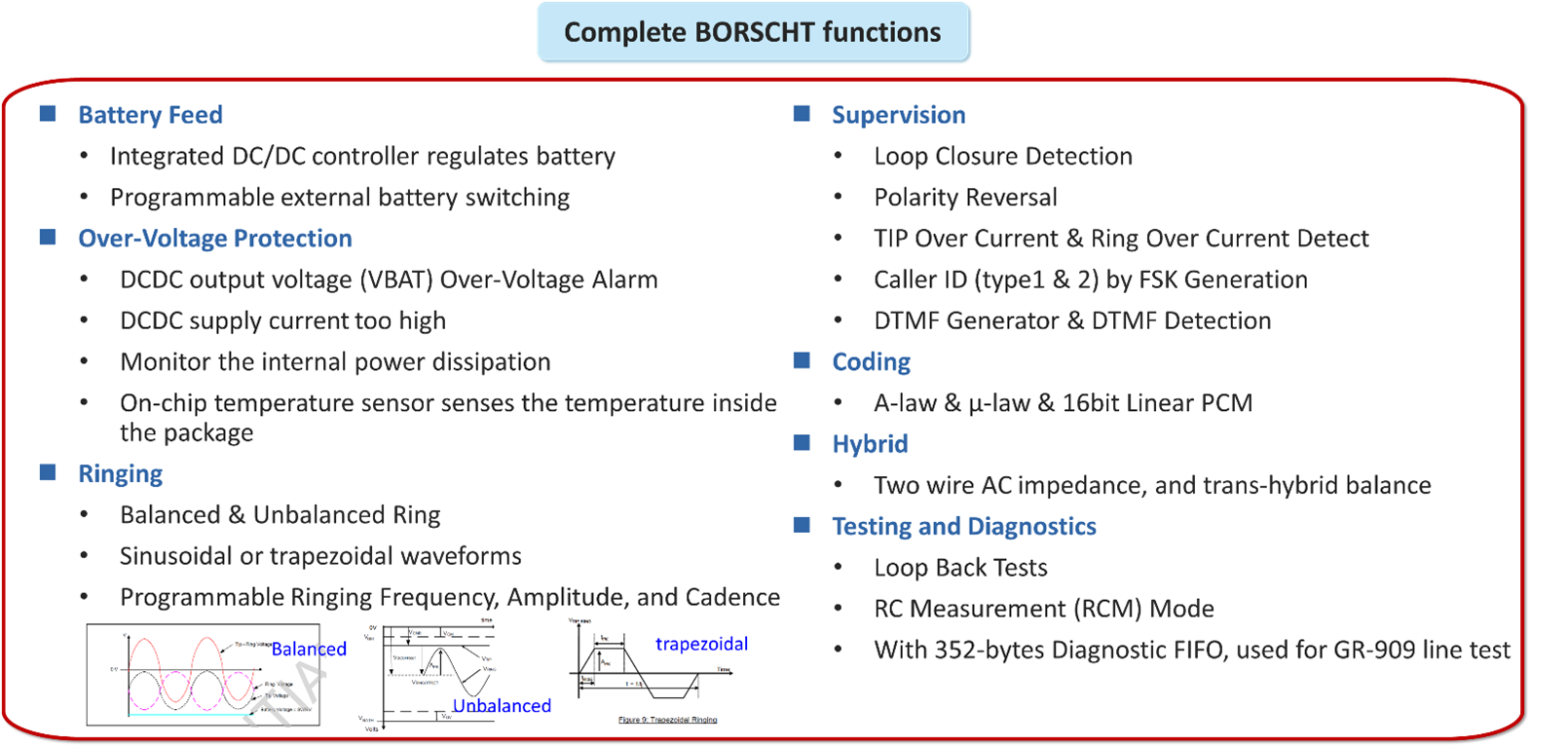
Nuvoton has introduced a new generation of communication port solution chips, Coslic (CODEC + Slic), integrating a programmable voice CODEC, telephone interface (Slic), and integrated Boost circuit in a single chip. This design effectively reduces power consumption and provides a complete single-channel and dual-channel FXS (Foreign Exchange Station) interface. The maximum negative voltage can support up to 120V, meeting BORSCHT characteristics, with SPI Bus and PCM channel, capable of receiving control commands and voice packets from the main control SOC.
Basic Functions:
Features:
- Highly integrated FXS interface with voice signals transmitted and received on the TIP and RING lines, providing feedback and status monitoring.
- Programmable ring current, feedback voltage, ring voltage, and ring interval.
- Adaptive control of the PWM duty cycle within the BOOST circuit for DC/AC adjustment.
- Compliance with international telecommunication standards ITU-T G.712 and ITU-T Q.552.
- Supports GR-909 line testing, automatically detecting voltage, telephone impedance, and telephone status.
- Built-in DTMF generator and decoder.
- Supports FSK caller ID display.
- Supports impedance matching models for significant countries.
Apart from FTTx applications, Coslic can be used in other communication fields, such as 4G CPE, PBX (Private Branch Exchange), optical transceivers, VoIP gateways, ATA adapters, and more. These products require Coslic to have FXS (Foreign Exchange Station) analog output capabilities.
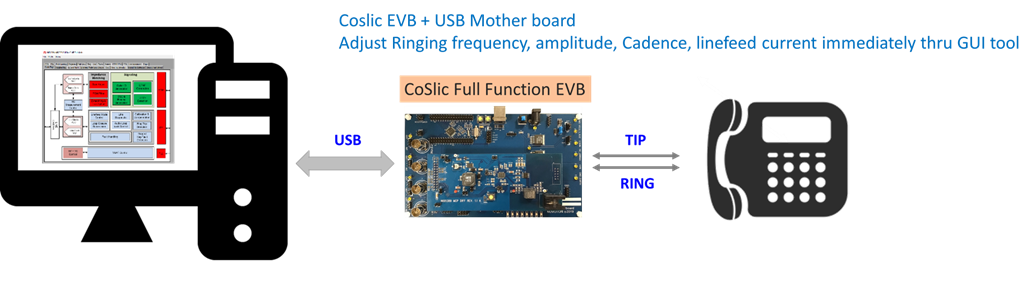
Development Tool:
To support customer project development, Nuvoton provides design and development tools, including development boards, software GUI, and related technical documentation. These tools assist customers in quickly developing specialized applications for different products (devices).
Coslic Series Product Roadmap: