How to Secure an IoT Application from MCU/MPU Perspectives
Internet of Things (IoT) security encompasses device security and network security, and under this definition covers the processes, technologies, and protective measures required to protect networked devices and networks. In today's society, various types of networked devices are becoming more and more popular, from industrial devices, smart grids, smart homes, entertainment and wearable devices, etc. Suppose the possible risks are not well thought out at the time of development to analyze and evaluate the threat model. It is easy to cause vulnerabilities in use and then be attacked by people to cause losses. For example, if industrial devices are attacked, it may cause danger to personnel or leakage of confidential information; if hackers control the smart grid, it will affect people's livelihood and industries; it happens to intelligent homes and entertainment, and the risk is that personal data will be stolen. Therefore, how to do an excellent job of security protection from the device itself is an item that must be carefully considered at the early stage of the design and planning of networked products.
IoT device security must protect the system, network, and data from a wide range of IoT security attacks, and these attacks can be divided into four types:
- Communication attacks for data transmission between IoT devices and servers.
- Lifecycle attacks on IoT devices from user to maintenance.
- Attacks on the internal software of the device.
- Physical attacks directly against the chip inside the device.
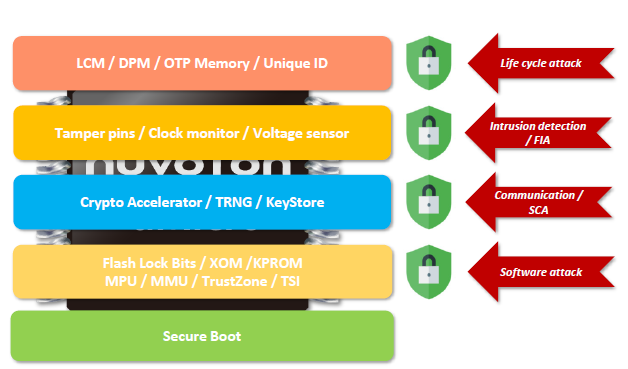
Well-designed secure IoT microcontrollers allow developers to protect devices from all types of loopholes. Nuvoton has been working diligently on microcontroller security in recent years. Last year the company launched a new generation of secure IoT microcontrollers, NuMicro® M2354, after the M2351 series, which optimizes the security features required for IoT devices. The microcontroller's internal hardware encryption accelerator allows data transmission between the device and the server to be encrypted, which helps to resist communication-type attacks and improves the key anti-theft capability when combined with the Key Store.
With the hardware-based lifecycle management technology, the various security services built under Trusted-Firmware-M can prevent lifecycle attacks.
The hardware isolation mechanism implemented in the microcontroller by the Trustzone technology can separate the execution environment into secure and non-secure memory, peripherals, and functions.
With the secure boot program provided by the microcontroller to verify the running software's integrity and legitimacy, software attacks can be prevented. Anti-tampering, anti-fault injection and side-channel attack technologies offer protection against non-intrusive physical attacks on the chip.
Platform Security Architecture (PSA) - which defined the security foundation for IoT devices and was proposed by Arm in 2017 to provide a clear framework for protecting and integrating the security of networked devices, from analysis to security assessment and authentication. Nuvoton's secure IoT microcontroller M2351 series passed PSA Certified Level 2 and PSA Functional API certifications for its security features in 2021, while the next generation M2354 series targeted to pass PSA Certified Level 3 certification is also actively in progress!