Safety Features and Applications of NuMicro M2351SF
NuMicro® M2351 Series
NuMicro® M2351 SeriesThe NuMicro® M2351 series microcontrollers are based on the Arm® Cortex®-M23 with built-in Armv8-M architecture TrustZone® technology, and provides XOM (Execute-Only-Memory) used to define the Execute-Only memory areas to protect key program codes; it is also the first microcontroller that passed the Arm® PSA Certified™ Level 1 and PSA Functional API Certified certifications. The operating frequency of the M2351 series microcontrollers can reach as high as 64 MHz and has 512 KB dual bank architecture flash memory built-in, able to support Over-The-Air (OTA) firmware upgrades, as well as 96 KB built-in SRAM. IoT security issues were also addressed. To make them compatible with the Arm® Platform Security Architecture (PSA), Nuvoton developed the Nuvoton Secure Microcontroller Platform (NuSMP). This platform fully defined the security functions of the NuMicro® microcontrollers based on the Arm® Cortex®-M series CPU and provides a wide range of optional microcontroller hardware security and software security functions. With these benefits, customers can easily perform security designs for IoT node equipment. In addition to the TrustZone® technology and NuSMP, the NuMicro® M2351 series is also equipped with abundant functions to increase system security. For example, The Secure Boot Loader can verify the integrity of the firmware, and support complete microcontroller firmware updates when needed. The hardware encryption accelerator including ECC supports encryption and decryption operations to reduce the computation loads of the processor. M2351 also provides diverse power management modes to make power consumption management more efficient. The power consumption of the M2351 series under normal LDO run mode is 97 μA/ MHz, and the power consumption under DC-DC mode is 45μA/ MHz. The current for their Standby-Power-down mode (SPD) is 2.8 μA, and the current for their Deep Power-down Mode (DPD) without VBAT is less than 2 μA. The M2351 series have both security and low-power features and is one of the best choices among the many IoT application solutions currently available on the market.
Why M2351SF
Next, we need to explain how important trust is for the millions of networking devices that are continually being developed, and why secure storage is one of the most important and necessary security functions. M2351SF provides higher security levels able to provide bigger secure storage for the codes and data of different application processes – 4M Bytes. The security of networking devices is determined by the mutual end-to-end identity verification during IoT cloud service connections, and to realize this security goal, it requires a series of powerful solutions including trusted activation, various keys, credentials, and certifications, etc. for the secure wireless updates of the firmware and software. Through the use of the Winbond secure flash solution, M2351SF can protect the codes and data of microcontrollers well to reduce the exposure of vulnerabilities. The secure Flash memory is dedicated to performing encrypted storage for the valuable assets of application processes such as biometric data, certificate authority data and system logs, etc. Also, unique binding is used between microcontrollers and the secure flash memory of M2351SF, as well as encrypted SPI interface for internal connections to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the microcontrollers’ digital assets. There are also great countermeasures for unauthorized attack operations such as Side-Channel Attack, Man-in-the-Middle, Rollback, Sniffing and Fault-Injection, etc. while data is being transmitted between the microcontroller and flash memory. Therefore, microcontroller system developers can easily design application processes for markets that have rigorous demands for security, such as the security industry, smart homes, smart cities, smart IoT and any other embedded equipment that have potential needs for large amounts of secure storage. In addition to enhancing the security of microcontroller storage, M2351SF still retained all security functions of the M2351 series, including the Armv8-M TrustZone®, execute-only memory (XOM), encryption hardware accelerator, secure debugging, system-level tamper detection pins and all software tools used for application process development; they are all identical to the M2351 series.
Main Applications of NuMicro®M2351SF
- Protect valuable software assets from being abused
In the past development processes of microcontroller application products, the most troublesome thing for independent software developers or system integrators is how to ensure the software assets inside the microcontrollers can be rigorously protected while allowing certain flexibility for software development for its partners. As shown in the example in Figure One, the Armv8-M architecture can place valuable communication protocols into the TrustZone or Secure Flash area, and the upper applications based on these communication protocols can be placed at different memory locations; this makes collaborative development easier for different development teams to create software individually on their specialized fields. Examples of this type of application include certain short-distance communication protocols, audio encoders, and biometric core algorithms, etc.
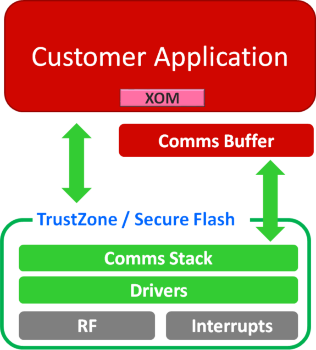
Figure One: TrustZone for Armv8-M / Secure Flash – Protect valuable middle software
- Ensure that each microcontroller application product is trusted and protected (Root of Trust)
In the foreseeable future of a networked environment world, there will only be more and more networked devices; and each of these devices is a potentially damaging intrusion point. Sensitive data might need to be stored on networked devices, and with the TrustZone and Secure Flash area, the ID, encryption key and software update of a single microcontroller can be protected in the secure area. Each time it boots up, self-check can be performed to ensure that the software running inside the device was not tampered with and that since the root point of the boot-up is a trusted entry point; only this can be called guaranteeing that the functions are normal. The explanations in Figure Two gave an illustrated example; this type of application includes applications related to media rights such as DRM (Digital Right Management), as well as the identification and communication between nodes for payments and networked environments.
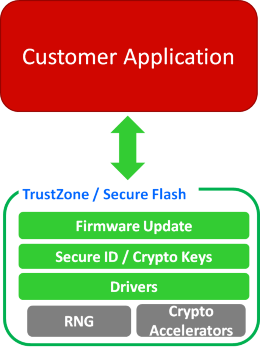
Figure Two: TrustZone for Armv8-M / Secure Flash – Root of Trust
- Guarantee the integrity of core software
Since the microcontroller market has shifted from the traditional 8-bit/16-bit to 32-bit in recent years, the increasingly powerful computing power allowed the equipping of richer peripheral resources such as higher capacity Flash and RAM, and this allowed small microcontroller applications to have more opportunities to run operating systems. These core software, whether OS or firmware, have risks of being attacked by malicious programs; also, there are no unified software-only security check standards for the software itself. Most of them are industry standards, such as ISO 26262 for the vehicle industry and IEC 61508 for the industrial industry; others include FDA for medical equipment and the Smart Metering that might be developed in the future, etc. Software developers need to put in a lot of effort to achieve the requirements for these standards. Now that it is TrustZone for Armv8-M and Secure Flash, even though these functions cannot be used to meet all industrial standards and specifications immediately, but the practice to build a TrustZone in the hardware can reduce the efforts of software developers to a certain extent, and it can increase the efficiency for the creation and maintenance of core software. Since the Armv8-M TrustZone architecture or Secure Flash can allow certified software to be safely protected, a sandboxing area is provided for software that does not need to be certified or that were outsourced to be developed. This also makes it more convenient for software personnel to provide technical support for different applications; for example, upper-level application software developers can be authorized to provide technical services for products, as explained in Figure 3.
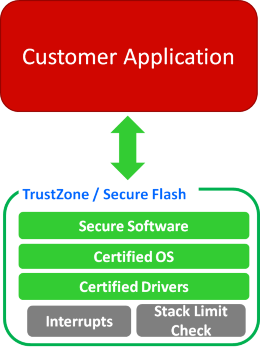
Figure 3: TrustZone for Armv8-M / Secure Flash – Sandboxing Certified Software